Japan withholding tax on the payment to Foreign company / Non-resident
Overview
A website of posting movies run by google, “YouTube”, announced that it will begin withholding federal income taxes on creators from June 2021, and creators’ revenue generated by viewers in the United States has been affected. Creators have been asked to submit their tax information for exemption under the Japan-US tax treaty.
In this case, google had deal with this payment to the creators as “advertisement charge”, however, changed to “Royalty”.
In Japan as well, the payment to non-residents should be withheld tax if it is subject to domestic source income. This time, we will explain the payment to non-residents that is difficult to judge if it should be withheld or not.
What is domestic source income?
Domestic source income is defined that income that concern business conducted in Japan, and Japanese tax law provides that the income will be withheld tax at the country where the business is conducted.
Permanent Establishment
For non-resident or non-resident corporation (Foreign company), the method of taxation depends on whether the non-resident or non-resident corporation have Permanent Establishment (PE) in Japan or not.
Scope of Permanent Establishment
- Place that conducts business such as branch offices, factories.
- Construction, installation, fabrication or other works, or provision of direction and supervision service of these works for over 1 year.
- Agents, who has right to contract agreements on behalf of non-residents.
Taxation of Corporation tax and Withholding tax for Non-resident Corporation
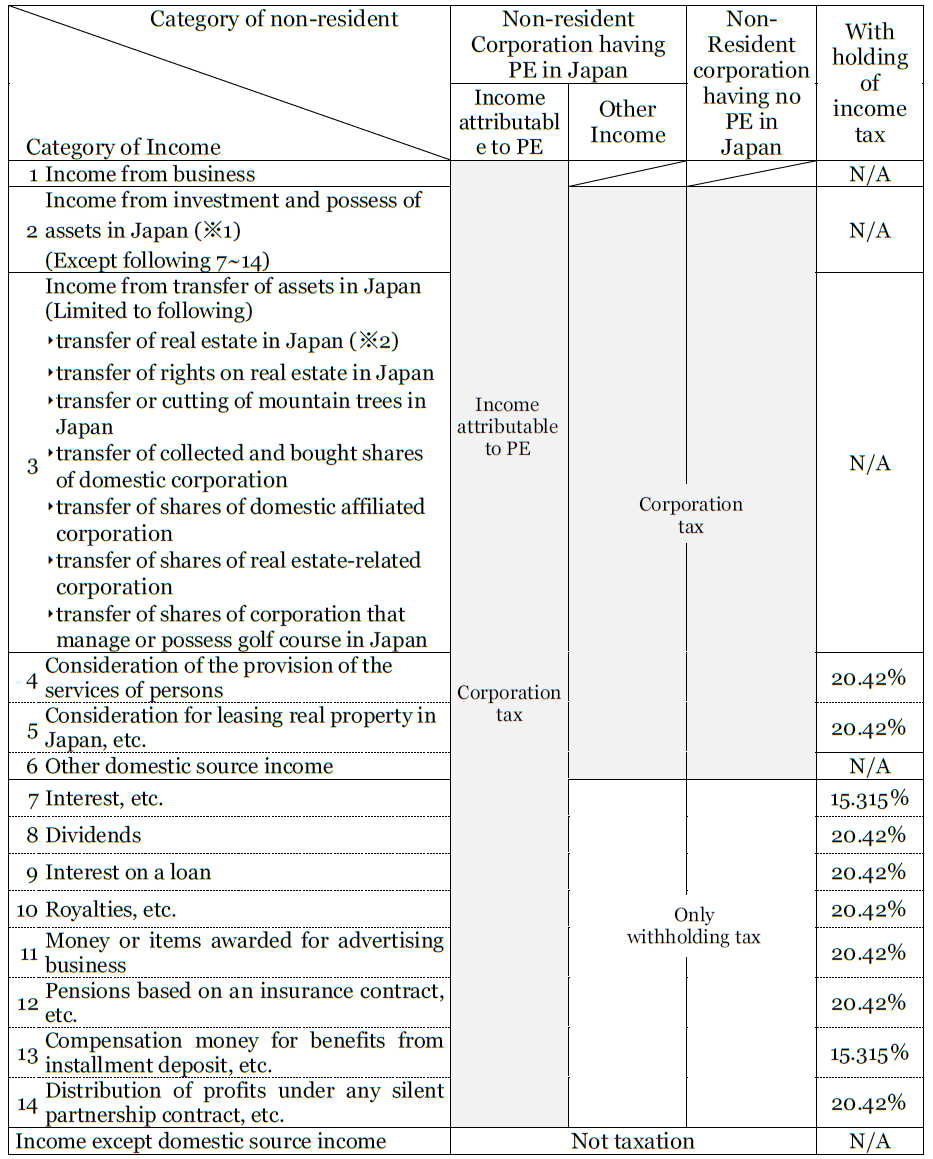
Shaded sections indicate income subject to tax return for non-resident in Japan.
(※1) Interest on short-term account receivable whom period of time is for less than 6 months is not subject to income from investment and possess of assets in Japan.
(※2) Among the transfer of real estates in Japan, consideration of land should be withheld 10.21% income tax.
When company in Japan pays non-resident for price of any products or services, the company should judge the category of payment (or income for non-resident).
Especially “Royalty” might make many companies worries.
Definition of Royalties, etc.
As sample, we will explain more details about how the royalty fee payment to non-resident is treated in Japan.
Under Japanese Tax Law, royalty treated as domestic source income is defined charge or consideration of use that non-resident receive from person who do business with in Japan such as following.
| A) | Royalty of industrial property right, etc. or consideration of transfer of the right Industrial property right, etc. is categorized the following further |
|
|
| B) | Royalty of copyright, or consideration of transfer of the right Making a copy/presentation/performance/broadcasting/exhibition/other use of copyrighted works, payment for setting of publishing right, consideration for transfer of copyright |
| C) | Charge of using mechanical device Machine, device, transportation vehicle, tools, etc. |
Case study
Here gives examples
Payment for license fee of patent right
Corporation A is a Japanese corporation, and doing business globally with using patent right of American corporation B which doesn’t have PE in Japan. The patent right is property of B and A will pay B 1milion JPY for use it.
- Examination if the payment is subject to the withholding system or not under Japanese Tax Law.
Firstly, we should investigate which income this payment is categorized out of non-resident income in Japan. The payment is consideration of use of patent right and subject to royalties as mentioned above A). Under Japanese Tax Law, A is required to deduct 20.42% withholding tax from the payment.
- Consideration of treatment in tax treaty
Once the payment is subject to withholding system, we need to look up the treatment in Japan-US tax treaty next.
Japan-US tax treaty
- “Royalties arising in a Contracting State and beneficially owned by a resident of the other Contracting State may be taxed only in that other Contracting State.”
⇒In other words, the payment is taxed in only the country where receiver of the payment is resident. For this case, only B is taxable and A is exempt.
- “The term “royalties” as used in this Article means payments of any kind received as a consideration for the use of, or the right to use, any copyright of literary, artistic or scientific work including cinematograph films and films or tapes for radio or television broadcasting, any patent, trade mark, design or model, plan, or secret formula or process, or for information concerning industrial, commercial or scientific experience.”
⇒The use of patent right is included to “Royalties” defined in the treaty.
- “The provisions of paragraph 1 shall not apply if the beneficial owner of the royalties, being a resident of a Contracting State, carries on business in the other Contracting State in which the royalties arise, through a permanent establishment situated therein, and the right or property in respect of which the royalties are paid is effectively connected with such permanent establishment.”
⇒If B has PE and does business in Japan, the payment would be business income in Japan, not “Royalties”. And in this case, B has no PE in Japan.
According to above, the withholding tax would be exempted with submission of application to tax office.
Application Form for Income Tax Convention
For reduction or exemption of withholding tax, it is required to submit “Application Form for Income Tax Convention” to tax office in Japan. Further if provision of tax treaty for application of reduction or exemption is subject to the limitation on benefits article, “Attachment Form for Limitation on Benefits Article” should be submitted as well with “Certificate of Residence” that is issued by the authorities of partner’s country. This special provision is adopted in the United States, the Great Britain, France, etc.
Internet Business has been developing with COVID-19 and the transaction between global business persons are increasing and being diversified today. In global transactions, problem of taxes between countries could occurs at lots of situations. if you will do business with non-Japanese corporation, you should examine how the payment would be treated under Japanese tax law or tax law of partner’s country before start of the transaction.
If you need further information, please contact us.